Raspberry Pi SIP Intercom
Sip intercom with a raspberry pi.
Here's an intercom system using a raspberry pi and an asterisk server. I have used the PJSIP library which also includes a library for Python called PJSUA.
My code: Download
Main features:
1- Sip protocol.
2- Low power.
3- G722 codec for wideband audio.
4- Class D amplifier.
5- Auto disconnect after a timeout.
6- Blinking push button while in standby.
7- Use of an ini file for SIP registration and audio settings.
8- USB Microphone ( I got mine by salvaging an old webcam)
HOW TO:
1- Install latest RASPBIAN LITE with Win32DiskImager:
https://www.raspberrypi.org/downloads/raspbian/
Setup wifi:
sudo nano /etc/network/interfaces# Include files from /etc/network/interfaces.d:
source-directory /etc/network/interfaces.d
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
iface eth0 inet dhcp
allow-hotplug wlan0
auto wlan0
iface wlan0 inet dhcp
wpa-ssid My_wifi_SSID
wpa-psk my_password
allow-hotplug wlan1
iface wlan1 inet manual
wpa-conf /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf
2- Enable SSH and change Timezone:
sudo raspi-configGo to option 5 (Interfacing options) and Enable SSH
Login to the pi with the following user and password:
User: pi
Password: raspberry
3- Update packages lists:
sudo apt-get update4- Install prerequisites:
sudo apt-get install rpi.gpio
sudo apt-get install alsa-base
sudo apt-get install alsa-tools
sudo apt-get install libasound2-plugins
sudo apt-get install libasound2-dev
sudo apt-get install libssl-dev
sudo apt-get install libv4l-dev
sudo apt-get install python-pip
sudo pip install asterisk-ami5- Install SDL (It takes a while to build...)
mkdir sdl
cd sdl
wget https://www.libsdl.org/release/SDL2-2.0.6.tar.gz
tar xvfz SDL*
cd SDL2-2.0.6/
./configure
make
sudo make install6- Install PJSIP: (Go drink a beer! This will take a while to compile....)
mkdir pjsip
cd pjsip/
wget http://www.pjsip.org/release/2.7/pjproject-2.7.tar.bz2
tar xvfj pj*
cd pjproject -2.7/
Edit config.h and add this to the end of file
#define PJMEDIA_AUDIO_DEV_HAS_ALSA 1
nano pjsip/pjproject-2.7/pjlib/include/pj/config.h./configure --disable-ffmpeg --disable-openh264 --disable-libwebrtc
make dep
make
sudo make install
sudo reboot7- Install PJSUA:
sudo apt-get install python-dev
cd pjsip/pjproject-2.7/pjsip-apps/src/python/
sudo python ./setup.py install8- Sound set-up. What a PITA in Linux...
What is my default soundcard?
Linux will start by checking /etc/asound.conf and if nothing is found, it will use the default card 0 found by typing this command:
cat /proc/asound/cardsex:
0 [ALSA ]: bcm2835 - bcm2835 ALSA
bcm2835 ALSA
1 [Device ]: USB-Audio - USB PnP Sound Device
C-Media Electronics Inc. USB PnP Sound Device at usb-20980000.usb-1.3, full spe
2 [U0x46d0x9a1 ]: USB-Audio - USB Device 0x46d:0x9a1
USB Device 0x46d:0x9a1 at usb-20980000.usb-1.4, high speed
Let's test card #1 directly to make sure it's working:
speaker-test -D hw:1,0 -c 2 -t sine -f 1000Some useful commands:
Display the card number of playback devices or detailed information:
aplay -l
aplay -LDisplay the card number of recording devices or detailed information:
arecord -l
arecord -LDisplay the name of volume and mic control:
amixerCommand to see the audio level (like in alsamixer) .My audio control is called Speaker:
amixer get -M SpeakerI want the USB device to be my default card.
I have created a new file called .asound.conf in my home user's directory.
IMPORTANT: Must use dmix as PCM device otherwise the soundcard cannot be shared.
pcm.!default
{
typeasym
# Playback device
playback.pcm
{
type plug
slave.pcm "dmix:1,0" # Run aplay -l and aplay -L
}
# Capture device
capture.pcm
{
type plug
slave.pcm "hw:2,0" # Run arecord -l
}
}
Edit the /boot/config.txt file to disable onboard sound on the PI:
sudo nano /boot/config.txtComment out the following line in /boot/config.txt:
# Enable audio (loads snd_bcm2835)
#dtparam=audio=on
9- Install WiringPi for reading GPIO (Optional):
sudo apt-get install git-core
git clone git://git.drogon.net/wiringPi
cd wiringPi
sudo ./build
sudo ldconfig
10- Dialplan setup in asterisk (extension.conf):
[internal]
;Calling a single intercom
exten => _2XXX,1,NoOp()
same => n,Dial(PJSIP/${EXTEN},20)
same => n,Hangup()
;Calling multiple intercom
exten => 2222,1,NoOp()
same => n,Dial(PJSIP/2004&PJSIP/2005,20)
same => n,Hangup()
11- AMI (manager.conf)
[general]
enabled = yes
webenabled = no
port = 5038
bindaddr = 192.168.0.6
[Auto_Dialer]
secret = sknfd67sndoasd8no89hdsfas
deny=0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0
permit=192.168.0.0/255.255.255.0
write = call,command,system,originateReload manager config and dialplan:
raspberrypi*CLI> module reload manager
raspberrypi*CLI> dialplan reloadCircuit:
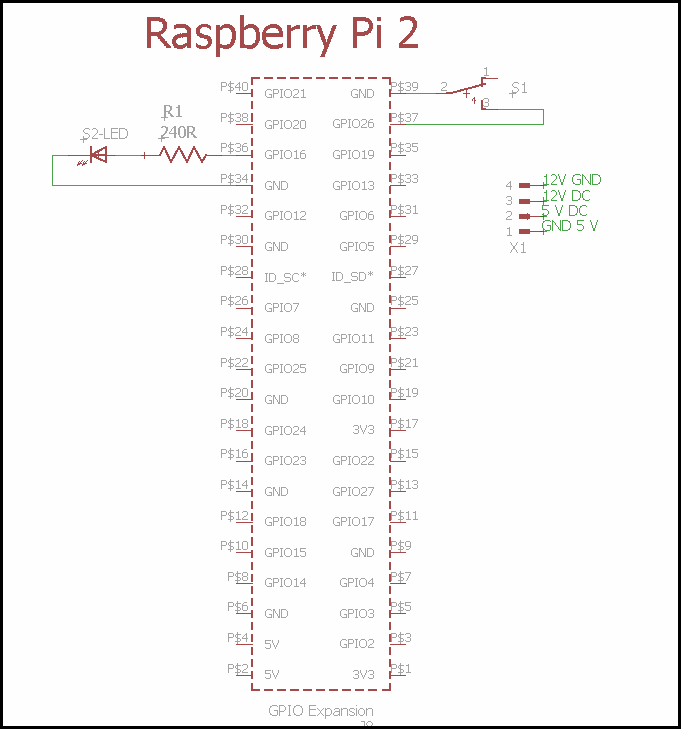
10- Run the script as a service with SystemD.
Create a file called Intercom_sip.service in /lib/systemd/system with the following:
[Unit]
Description=Intercom SIP Service
After=multi-user.target
[Service]
Type=simple
ExecStart=/home/pi/Intercom/Pi-Intercom.py
User=pi
WorkingDirectory=/home/pi/Intercom
StandardOutput=null
Restart=always
RestartSec=3
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
sudo chmod 644 /lib/systemd/system/Intercom_sip.service
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl enable Intercom_sip.serviceStart and stop the service:
sudo systemctl start Intercom_sip.service
sudo systemctl status Intercom_sip.service
sudo systemctl stop Intercom_sip.service
DEBUG INFO:

